#2 - with my repetitive strain injury solution number 2 I tried to support my wrist directly with a wrist splint. This was exactly what my doctor recommened to my Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI).
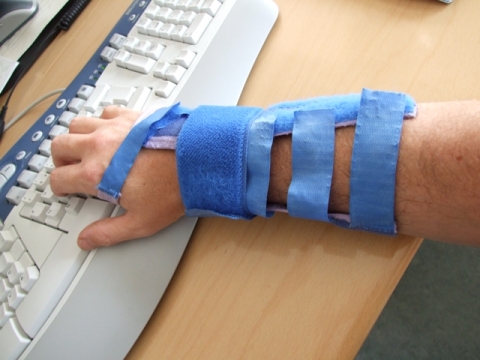
The “feeling” on keyboard writing and mouse operations is some kind of strange at the beginning. The first days I really thought this might help my on my repetitive strain injury problem. But as mentioned before:
You have to change the causation, not the sympthoms!
In my personal oppinion - this wrest splint is only lowering the sympthoms - little lowering of wrist pain. But you should really think about changing the causation…
So I had to find some other repetitive strain injury solutions. In fact I found 10 solutions. Read more on repetitive strain injury solution #3 -rest your injured wrist on a supporting mouse or keyboard pad.
••• Also read my complete repetitive strain injury medical history compendium and my solution abstract
Wiederholte Belastungsverletzung Lösung 🔗
Als ich versuchte, meine wiederholte Belastungsverletzung zu behandeln, probierte ich, eine medizinische Handgelenkschiene zu tragen. Mein Arzt empfahl mir, mein Handgelenk direkt mit einer Handgelenkschiene zu unterstützen. Am Anfang fühlte es sich beim Tippen auf der Tastatur und bei der Mausbedienung seltsam an.
Die ersten Tage dachte ich wirklich, dass dies mein Handgelenkschmerz verbessern könnte. Aber wie bereits erwähnt, muss man die Ursache ändern, nicht die Symptome. Meiner persönlichen Meinung nach lindert diese Handgelenkschiene nur die Symptome leicht und verringert den Handgelenksschmerz. Man sollte wirklich über eine Änderung der Ursache nachdenken.
Deshalb musste ich nach anderen Lösungen für meine wiederholte Belastungsverletzung suchen. Tatsächlich fand ich Lösungen, bei denen man das verletzte Handgelenk auf einer unterstützenden Maus- oder Tastaturunterlage ruhen lassen sollte.
Eine feine Lösung für Computerbenutzer mit Handgelenkschmerzen und dem Karpaltunnelsyndrom ist mein vollständiges medizinisches Geschichtskompendium zur wiederholten Belastungsverletzung und mein Lösungsabstract für ein Karpaltunnelsyndrom. Man kann mehr über die Lösung für wiederholte Belastungsverletzungen erfahren, indem man das verletzte Handgelenk auf einer unterstützenden Maus- oder Tastaturunterlage ruhen lässt.
Aktualisierung für 2024 🔗
Im Jahr 2024 hat sich die Art und Weise, wie wir mit wiederholten Belastungsverletzungen umgehen, weiterentwickelt. Handgelenksschienen bleiben nach wie vor eine Option zur Linderung von Symptomen, aber es wird immer deutlicher, dass die Änderung der Ursache entscheidend ist. Neue Technologien und ergonomische Lösungen haben dazu beigetragen, dass Computerbenutzer mit Handgelenkschmerzen und Karpaltunnelsyndrom effektivere Behandlungsmöglichkeiten haben.
Die Bedeutung einer unterstützenden Maus- oder Tastaturunterlage für die Ruhe des verletzten Handgelenks wird weiterhin betont, da dies dazu beiträgt, die Belastung zu verringern. Es ist wichtig, dass Betroffene ganzheitliche Lösungen für wiederholte Belastungsverletzungen in Betracht ziehen und nicht nur kurzfristige Symptomlinderungen anstreben.
Insgesamt hat sich das Verständnis für wiederholte Belastungsverletzungen und deren Behandlung im Jahr 2024 weiterentwickelt, und es stehen den Betroffenen mehr Möglichkeiten zur Verfügung, um langfristige Verbesserungen zu erzielen.
Repetitive Strain Injury Solution: Using a Medical Wrist Splint 🔗
In the journey to find relief for repetitive strain injury (RSI), many individuals turn to using a medical wrist splint for support. This article will guide you through the process of using a wrist splint effectively to manage RSI symptoms and promote recovery.
Understanding the Importance of a Wrist Splint 🔗
A wrist splint is designed to provide stabilization and support to the wrist joint, reducing strain and pain during activities that aggravate RSI symptoms. It can help maintain proper alignment of the wrist, alleviate pressure on the median nerve, and prevent further damage to the affected area.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Wrist Splint for RSI 🔗
-
Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before using a wrist splint, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it is the right solution for your specific RSI condition.
-
Proper Fit: Make sure the wrist splint fits comfortably and securely on your wrist without restricting movement or causing discomfort.
-
Wear as Recommended: Follow the recommendations of your healthcare provider on when and how long to wear the wrist splint. Typically, it is recommended to wear it during activities that trigger RSI symptoms or while resting.
-
Maintain Good Posture: Use the wrist splint in conjunction with ergonomic practices to maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the wrist and surrounding muscles.
-
Consistent Use: Use the wrist splint consistently as directed to experience its full benefits and support your recovery from RSI.
Conclusion: The Future of RSI Management in 2025 🔗
In 2025, the approach to managing repetitive strain injuries has evolved to focus on holistic solutions that address the root cause rather than just symptom relief. Wrist splints continue to play a role in symptom management, but the emphasis is on incorporating ergonomic practices, technological advancements, and comprehensive treatment plans to achieve long-term improvements in RSI conditions.
By understanding the importance of using a wrist splint effectively and in conjunction with other interventions, individuals with RSI can optimize their recovery and enhance their overall well-being in the digital age.
Remember, seeking professional guidance and staying informed about the latest advancements in RSI management can empower you to take control of your health and prevent future complications.